-
Drones
-
 Top pick HS900 48MP | 4K@30fps | 3-Axis | Fast Charge HS790 3-Axis | 6K | 9 km HS600D 3-Axis | 48MP | 4K@30fps HS600 2-Axis + EIS | 3 km | 4K SonyView all →
Top pick HS900 48MP | 4K@30fps | 3-Axis | Fast Charge HS790 3-Axis | 6K | 9 km HS600D 3-Axis | 48MP | 4K@30fps HS600 2-Axis + EIS | 3 km | 4K SonyView all → Top pick HS440 Camera drone without GPS for backyard time HS360S GPS, 3KM Range, 4K camera drone HS360D 4K | 6 km | 80 min Flight HS360E 4K EIS | 6 km | HS280D Skill-Trainer Drone • 1080P 2 Batteries • Brushless Motors HS175G 4K@30fps | EIS | 60 min HS175D Pilot-friendly, GPS, 4K, Brushless MotorsView all →
Top pick HS440 Camera drone without GPS for backyard time HS360S GPS, 3KM Range, 4K camera drone HS360D 4K | 6 km | 80 min Flight HS360E 4K EIS | 6 km | HS280D Skill-Trainer Drone • 1080P 2 Batteries • Brushless Motors HS175G 4K@30fps | EIS | 60 min HS175D Pilot-friendly, GPS, 4K, Brushless MotorsView all →
-
- Accessories
- Blog
-
Support
-
Product SupportSpecs/Downloads/Tutorial Videos/FAQ
- HS900 Support
- HS790 Support
- HS720R Support
- HS720G Support
- HS720E Support
- HS720-4K Support
- HS710 Support
- HS700E Support
- HS600D Support
- HS600 Support
- HS110G Support
- HS460 Support
- HS440G Support
- HS440D Support
- HS440 Support
- HS430 Support
- HS420 Support
- HS360E Support
- HS360S Support
- HS290 Support
- HS280D Support
- HS190 Support
- HS175G Support
- HS175D Support
- View all →
-
- About








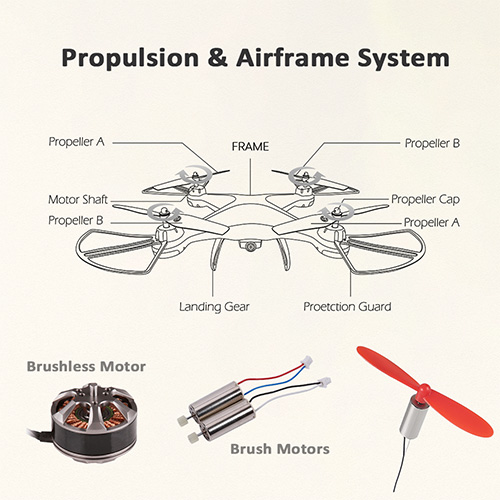
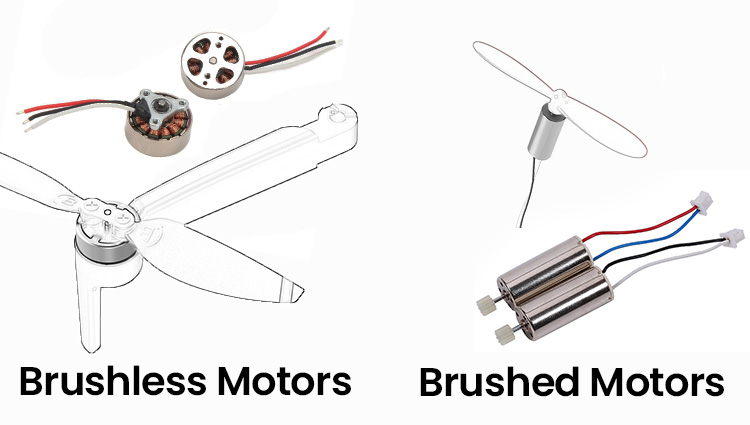
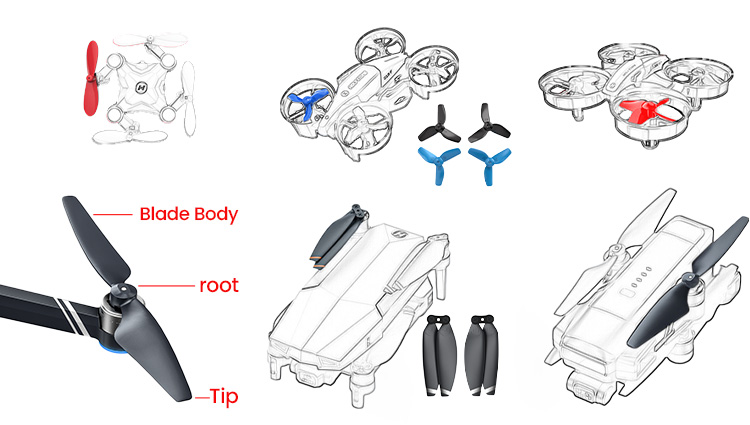
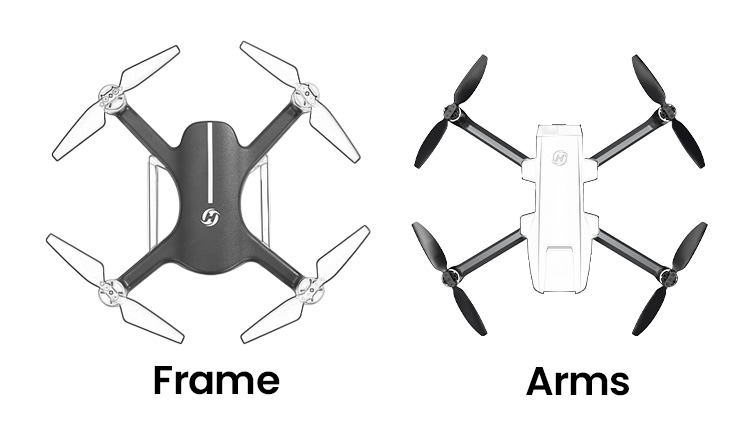

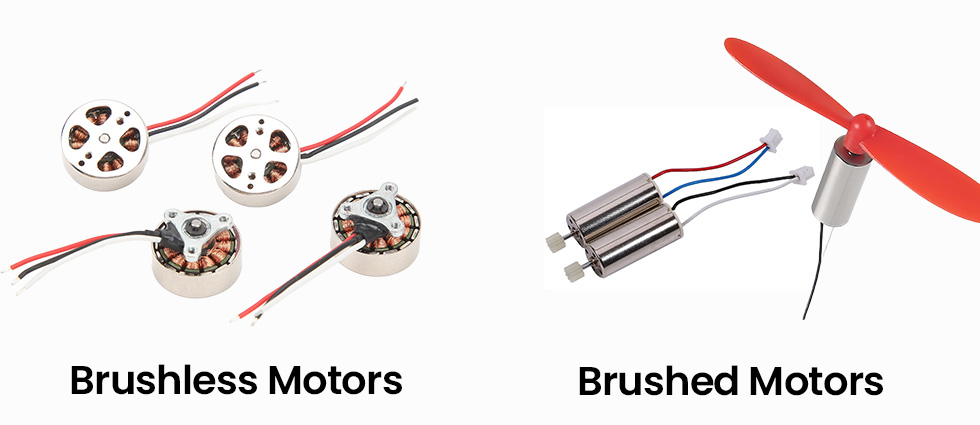
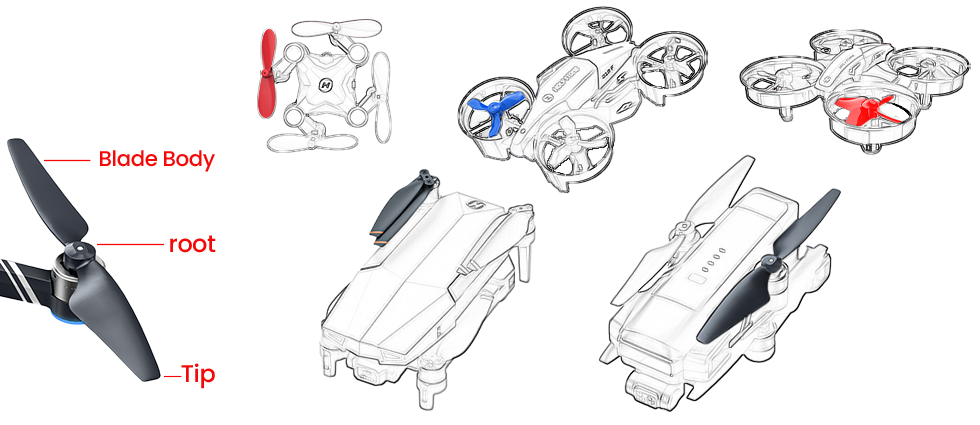
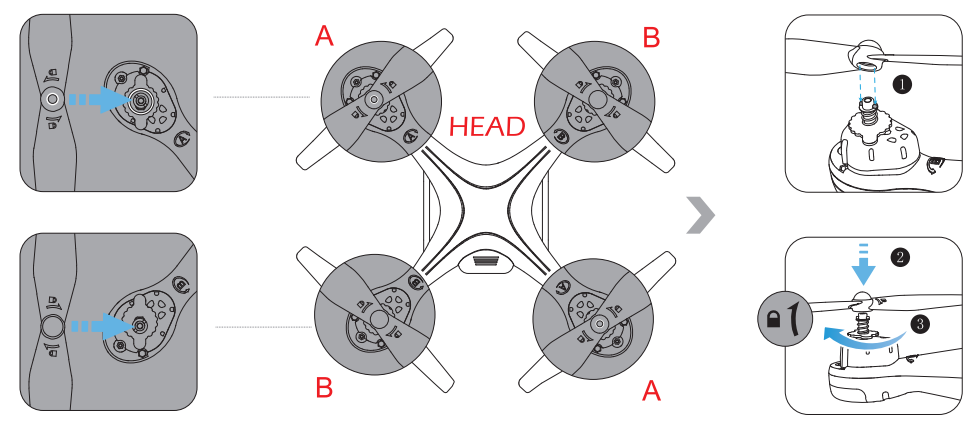
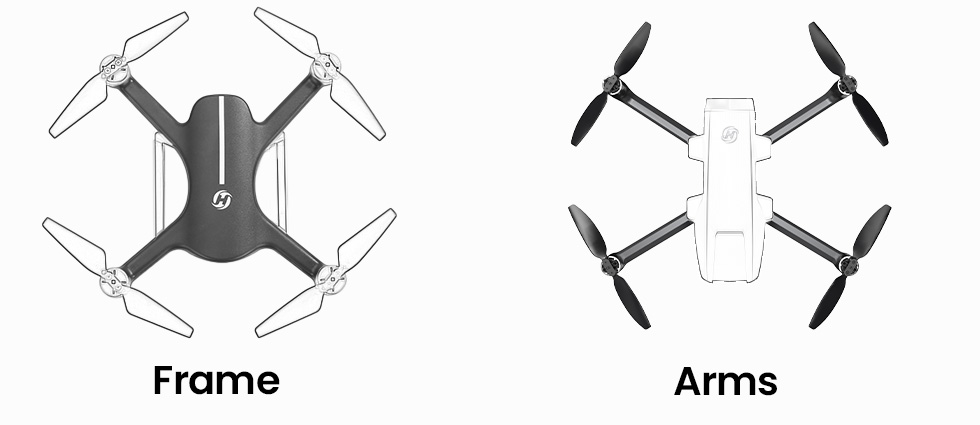
COMMENTS